ROSbot XL: Control Theory Applied
Designing and Testing Two PID Controllers for Robot Navigation
06 May 2024
Introduction
This in an advanced project focused on fine-tuning two PID controllers to guide a mobile robot through a maze efficiently. Utilizing the CyberLab environment, the project was developed using the Rosbot XL, a holonomic mobile robot. The main objective is to write, implement, and optimize PID controllers that enable the robot to accurate navigate within time and energy constraints
Objectives
- Acquire the coordinates of each waypoint within the maze.
- Develop and tune a PID controller to move the robot forward to each waypoint.
- Create and refine a PID controller to turn the robot toward the next waypoint.
- Combine both PID controllers to form a maze-solving program.
- Test the entire solution in the CyberLab real robot lab.
Tools and Technologies
- Programming Languages: C++
- Frameworks and Libraries: ROS2
- Simulation Environment: Gazebo
- Version Control: Git
Source Code
Process and Development
Preliminary Task: Acquire the Waypoint Coordinates
Using the teleop keyboard package, the Rosbot XL is manually guided through the maze. Coordinates for each waypoint are retrieved from the /rosbot_xl_base_controller/odom topic and recorded for subsequent programming tasks.
Part 1: Write a PID Controller to Move the Robot Forward
A distance controller is created using a ROS2 package named distance_controller. The controller reads odometry data and generates velocity commands to move the robot forward to predefined goals of 1m, 2m, and 3m distances. The PID parameters are carefully adjusted to prevent overshooting or undershooting targets while maintaining high speed.
Part 2: Write a PID Controller to Turn the Robot to Face the Next Waypoint
The turn_controller package is implemented to turn the Rosbot XL toward subsequent waypoints. Angular velocity commands are computed using a PID controller to rotate the robot precisely toward the next coordinate while avoiding overshooting.
Part 3: Testing Rotation in the CyberLab Real Robot Lab
The turn_controller is tested with the physical Rosbot XL in CyberLab. New waypoints are collected using the keyboard teleop, and the PID controller is adjusted to function under real-world conditions.
Part 4: Write a Program to Solve the Maze Using Two PIDs
A unified pid_maze_solver package combines the turning and distance controllers to guide the Rosbot XL through the maze efficiently. The robot alternates between turning and moving states as it progresses through each waypoint. The controllers are finely tuned to maintain alignment while moving forward.
Part 5: Testing Everything in the CyberLab Real Robot Lab
The final maze-solving program is tested and fine-tuned with the physical robot. YAML files with waypoint coordinates for both the simulated and real-world environments enable switching seamlessly between them.
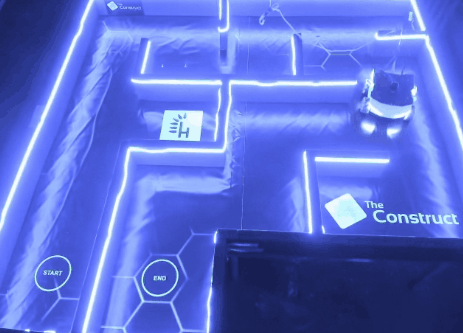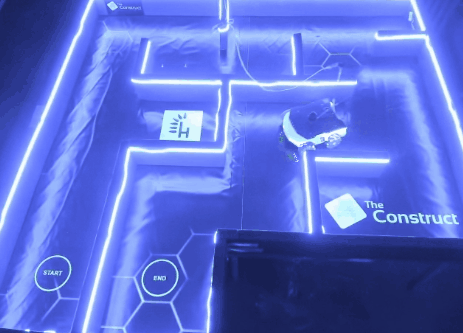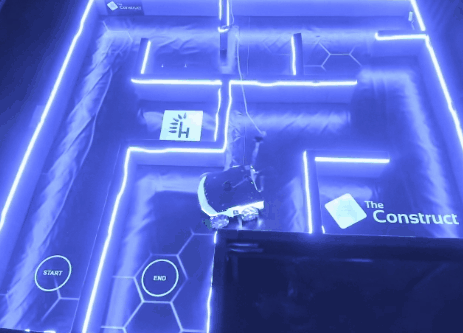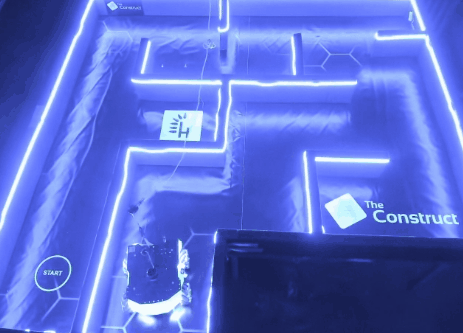
Results
The project successfully guided the Rosbot XL through the maze using optimized PID controllers. Testing both in simulation and the CyberLab lab ensured accurate calibration. The ability to alternate between two environments allowed thorough validation.
Key Insights
- Leveraging two PID controllers in sequence is effective for maze navigation.
- CyberLab provides a realistic environment for testing and refining control algorithms.
- YAML-CPP allows flexible waypoint management between simulation and real-world scenarios.